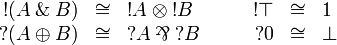Semantics
From LLWiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Additive structure: diagonal) |
m (notation for isomorphismes \cong instead of \sim) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
\begin{array}{rclcrcl} |
\begin{array}{rclcrcl} |
||
A\biorth &=& A\\ |
A\biorth &=& A\\ |
||
| − | (A\tens B)\orth &\sim& A\orth\parr B\orth &\quad& \one\orth &\sim& \bot\\ |
+ | (A\tens B)\orth &\cong& A\orth\parr B\orth &\quad& \one\orth &\cong& \bot\\ |
| − | (A\parr B)\orth &\sim& A\orth\tens B\orth &\quad& \bot\orth &\sim& \one\\ |
+ | (A\parr B)\orth &\cong& A\orth\tens B\orth &\quad& \bot\orth &\cong& \one\\ |
| − | (A\with B)\orth &\sim& A\orth\plus B\orth &\quad& \top\orth &\sim& \zero\\ |
+ | (A\with B)\orth &\cong& A\orth\plus B\orth &\quad& \top\orth &\cong& \zero\\ |
| − | (A\plus B)\orth &\sim& A\orth\with B\orth &\quad& \zero\orth &\sim& \top\\ |
+ | (A\plus B)\orth &\cong& A\orth\with B\orth &\quad& \zero\orth &\cong& \top\\ |
| − | (\oc A)\orth &\sim& \wn A\orth\\ |
+ | (\oc A)\orth &\cong& \wn A\orth\\ |
| − | (\wn A)\orth &\sim& \oc A\orth\\[1ex] |
+ | (\wn A)\orth &\cong& \oc A\orth\\[1ex] |
| − | A\limp B &\sim& A\orth\parr B\\ |
+ | A\limp B &\cong& A\orth\parr B\\ |
| − | A\limp B &\sim& B\orth\limp A\orth\\ |
+ | A\limp B &\cong& B\orth\limp A\orth\\ |
\end{array} |
\end{array} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<math> |
<math> |
||
\begin{array}{rcl} |
\begin{array}{rcl} |
||
| − | A\tens\one &\sim& \one\tens A\sim A\\ |
+ | A\tens\one &\cong& \one\tens A\cong A\\ |
| − | A\parr\bot &\sim& \bot\parr A\sim A\\ |
+ | A\parr\bot &\cong& \bot\parr A\cong A\\ |
| − | A\with\top &\sim& \top\with A\sim A\\ |
+ | A\with\top &\cong& \top\with A\cong A\\ |
| − | A\plus\zero &\sim&\zero\plus A\sim A\\ |
+ | A\plus\zero &\cong&\zero\plus A\cong A\\ |
\end{array} |
\end{array} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
<math> |
<math> |
||
\begin{array}{rcl} |
\begin{array}{rcl} |
||
| − | A\tens B &\sim& B\tens A\\ |
+ | A\tens B &\cong& B\tens A\\ |
| − | A\parr B &\sim& B\parr A\\ |
+ | A\parr B &\cong& B\parr A\\ |
| − | A\with B &\sim& B\with A\\ |
+ | A\with B &\cong& B\with A\\ |
| − | A\plus B &\sim& B\plus A\\ |
+ | A\plus B &\cong& B\plus A\\ |
\end{array} |
\end{array} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
<math> |
<math> |
||
\begin{array}{rcl} |
\begin{array}{rcl} |
||
| − | (A\tens B)\tens C &\sim& A\tens(B\tens C)\\ |
+ | (A\tens B)\tens C &\cong& A\tens(B\tens C)\\ |
| − | (A\parr B)\parr C &\sim& A\parr(B\parr C)\\ |
+ | (A\parr B)\parr C &\cong& A\parr(B\parr C)\\ |
| − | (A\with B)\with C &\sim& A\with(B\with C)\\ |
+ | (A\with B)\with C &\cong& A\with(B\with C)\\ |
| − | (A\plus B)\plus C &\sim& A\plus(B\plus C)\\ |
+ | (A\plus B)\plus C &\cong& A\plus(B\plus C)\\ |
\end{array} |
\end{array} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
<math> |
<math> |
||
\begin{array}{rclcrcl} |
\begin{array}{rclcrcl} |
||
| − | A\tens(B\plus C) &\sim& (A\tens B)\plus(A\tens C) &\quad& |
+ | A\tens(B\plus C) &\cong& (A\tens B)\plus(A\tens C) &\quad& |
| − | A\tens\zero &\sim& \zero\\ |
+ | A\tens\zero &\cong& \zero\\ |
| − | A\parr(B\with C) &\sim& (A\parr B)\with(A\parr C) &\quad& |
+ | A\parr(B\with C) &\cong& (A\parr B)\with(A\parr C) &\quad& |
| − | A\parr\top &\sim& \top\\ |
+ | A\parr\top &\cong& \top\\ |
\end{array} |
\end{array} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
<math> |
<math> |
||
\begin{array}{rclcrcl} |
\begin{array}{rclcrcl} |
||
| − | \oc(A\with B) &\sim& \oc A\tens\oc B &\quad& \oc\top &\sim& \one\\ |
+ | \oc(A\with B) &\cong& \oc A\tens\oc B &\quad& \oc\top &\cong& \one\\ |
| − | \wn(A\plus B) &\sim& \wn A\parr\wn B &\quad& \wn\zero &\sim& \bot\\ |
+ | \wn(A\plus B) &\cong& \wn A\parr\wn B &\quad& \wn\zero &\cong& \bot\\ |
\end{array} |
\end{array} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
Revision as of 09:45, 19 October 2009
Linear Logic has numerous semantics some of which are described in details in the next sections. We give here an overview of the common properties that one may find in most of these models. We will denote by  the fact that there is a canonical morphism from A to B and by A˜B the fact that there is a canonical isomorphism between A and B. By "canonical" we mean that these (iso)morphisms are natural transformations.
the fact that there is a canonical morphism from A to B and by A˜B the fact that there is a canonical isomorphism between A and B. By "canonical" we mean that these (iso)morphisms are natural transformations.
Contents |
Linear negation
![\begin{array}{rclcrcl}
A\biorth &=& A\\
(A\tens B)\orth &\cong& A\orth\parr B\orth &\quad& \one\orth &\cong& \bot\\
(A\parr B)\orth &\cong& A\orth\tens B\orth &\quad& \bot\orth &\cong& \one\\
(A\with B)\orth &\cong& A\orth\plus B\orth &\quad& \top\orth &\cong& \zero\\
(A\plus B)\orth &\cong& A\orth\with B\orth &\quad& \zero\orth &\cong& \top\\
(\oc A)\orth &\cong& \wn A\orth\\
(\wn A)\orth &\cong& \oc A\orth\\[1ex]
A\limp B &\cong& A\orth\parr B\\
A\limp B &\cong& B\orth\limp A\orth\\
\end{array}](/mediawiki/images/math/9/a/4/9a4031daae652e46533517511236351e.png)
Neutrals
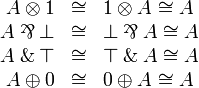
Commutativity
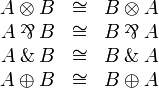
Associativity
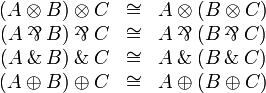
Multiplicative semi-distributivity
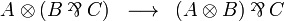
Multiplicative-additive distributivity
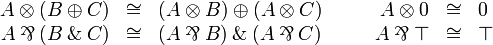
Additive structure
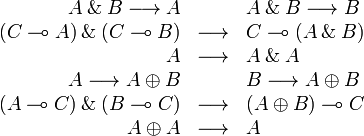
Exponential structure

Monoidality of exponential
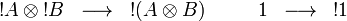
The exponential isomorphism