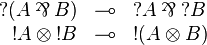Provable formulas
From LLWiki
(Difference between revisions)
m (→Monoidality of exponential: Duals added) |
(→Monoidality of exponential: Units removed: special case of equivalence for positive/negative formula) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<math> |
<math> |
||
| − | \begin{array}{rclcrcl} |
+ | \begin{array}{rcl} |
| − | \wn(A\parr B) &\limp& \wn A\parr\wn B &\quad& |
+ | \wn(A\parr B) &\limp& \wn A\parr\wn B \\ |
| − | \wn\bot &\limp& \bot \\ |
+ | \oc A\tens\oc B &\limp& \oc(A\tens B) |
| − | \oc A\tens\oc B &\limp& \oc(A\tens B) &\quad& |
||
| − | \one &\limp& \oc\one \\ |
||
\end{array} |
\end{array} |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
Revision as of 18:55, 28 October 2013
This page is a stub and needs more content.
Important provable formulas are given by isomorphisms and by equivalences.
In many of the cases below the converse implication does not hold.
Contents |
Distributivities
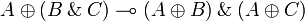
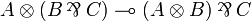
Factorizations
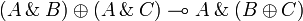
Additive structure

Exponential structure
Provable formulas involving exponential connectives only provide us with the lattice of exponential modalities.

Monoidality of exponential